Yellow Banana, with their vibrant yellow color and sweet taste, are one of the world’s most beloved fruits. [1]
Originating from the tropical regions of Southeast Asia, these fruits have not only become a global culinary staple but also boast a myriad of health benefits.
In this article, we will explore the origins, uses, characteristics, nutritional values, and health benefits of the yellow banana.

Origin of Yellow Banana
The journey of the yellow banana begins in the tropical regions of Southeast Asia, where the first domestication of bananas is believed to have taken place.
Over time, they spread to other parts of the world through trade and exploration. Today, bananas are grown in various tropical and subtropical regions across the globe, making them accessible to people worldwide.
Uses of Yellow Banana
- Beyond being a convenient and portable snack, bananas are a popular ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes.
- They can be sliced onto cereal, blended into smoothies, baked into bread and muffins, or simply enjoyed on their own.
- Bananas are a key component in desserts like banana splits and banana pudding.
- The fruit’s creamy texture and natural sweetness make it a favorite among both chefs and home cooks.
Characteristics of Yellow Banana
- The yellow banana is characterized by its vibrant yellow color when ripe. The peel is easily distinguishable, providing protection to the soft fruit within.
- Elongated and slightly curved, the banana typically follows a gentle, natural curve.
- The fruit boasts a smooth and creamy texture when ripe, making it enjoyable to eat both on its own and in various dishes.
- Harvested while still green and firm, bananas gradually ripen, turning yellow as they mature.
- The peel becomes thinner and easier to remove as the fruit ripens.
- Bananas come in various sizes, but they generally range from 6 to 8 inches in length.
- The inner flesh of the yellow banana is soft, white, and tender. As the banana ripens, the flesh becomes sweeter and takes on a more pronounced aroma.
- Ripe bananas emit a sweet, tropical fragrance, indicating their readiness for consumption.
- Like most cultivated bananas, the yellow banana is seedless, with tiny, vestigial seeds that are not typically noticeable when eating.
Nutritional Values of Yellow Banana
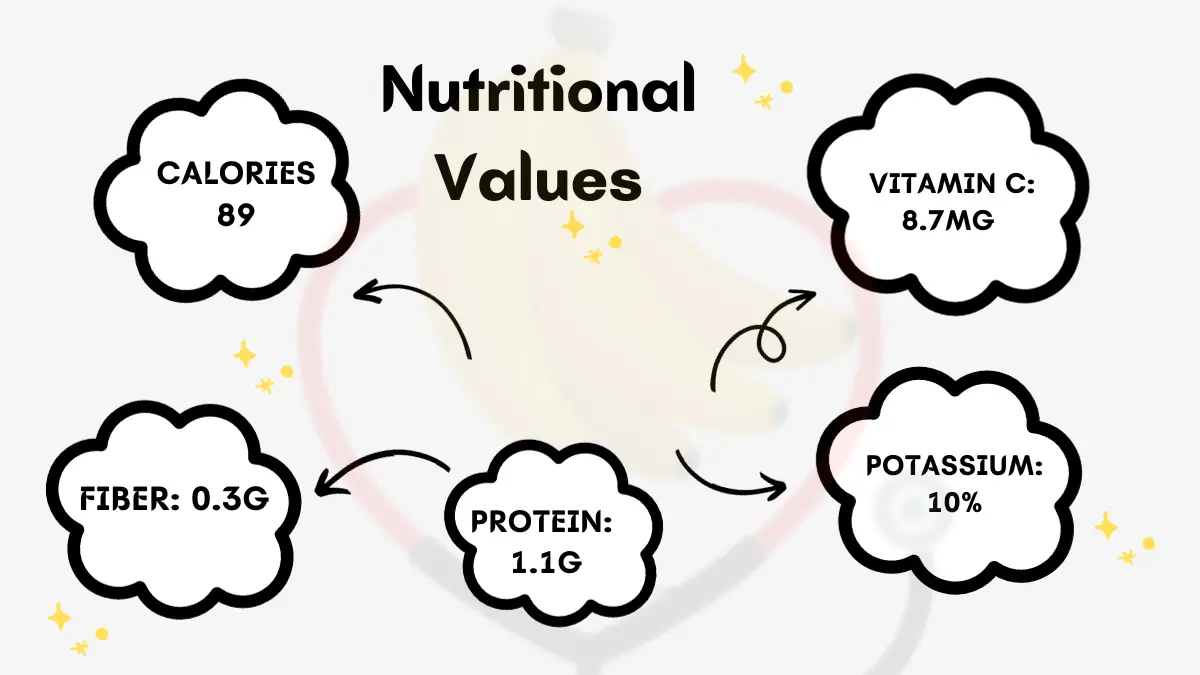
- Calories: 89
- Water: 74%
- Protein: 1.1g
- Carbohydrates: 22.8g
- Sugars: 12.2g
- Dietary fiber: 2.6g
- Fat: 0.3g
- Vitamin C: 8.7mg (15% of the daily recommended intake)
- Potassium: 358mg (10% of the daily recommended intake)
- Vitamin B6: 0.4mg (20% of the daily recommended intake)
- Magnesium: 27mg (8% of the daily recommended intake)
Health Benefits of Yellow Banana
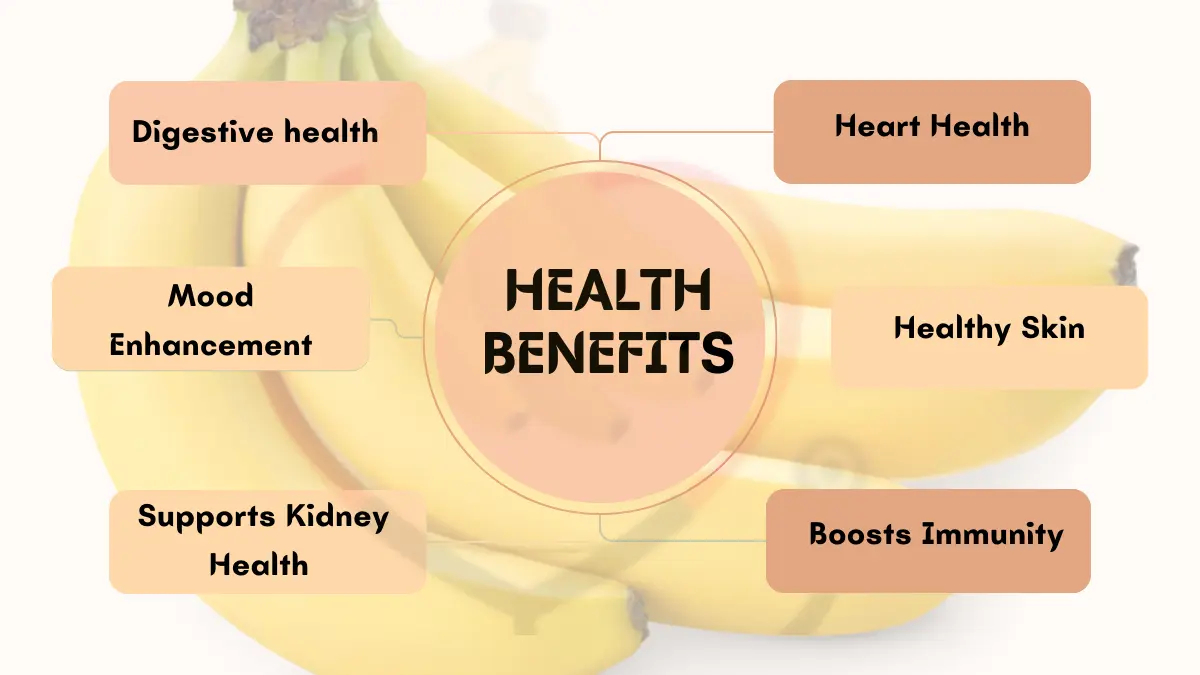
1: Rich in Nutrients
Bananas are a good source of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, vitamin B6, and magnesium.
2: Heart Health
The high potassium content in bananas is linked to lower blood pressure, promoting heart health and reducing the risk of stroke.
3: Digestive Health
The dietary fiber in bananas aids in digestion, preventing constipation and promoting a healthy gut.
4: Energy Boost
The natural sugars in bananas, particularly glucose, fructose, and sucrose, provide a quick and sustained energy boost, making them an excellent pre-workout snack.
5: Mood Enhancement
Bananas contain tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. Consuming bananas may contribute to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression.
6: Supports Kidney Health
The potassium in bananas helps regulate fluid balance, which is essential for kidney health.
Yellow banana is not just a delicious and versatile fruit; it’s a nutritional powerhouse with numerous health benefits. Whether enjoyed on its own or incorporated into various dishes, the banana remains a timeless favorite that contributes to a healthy and balanced diet.

